Each
and every Policy that we deal with in Insurance Brokerage is associated with
a Policy type and we list the Policy Types on the Policy Type Master. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
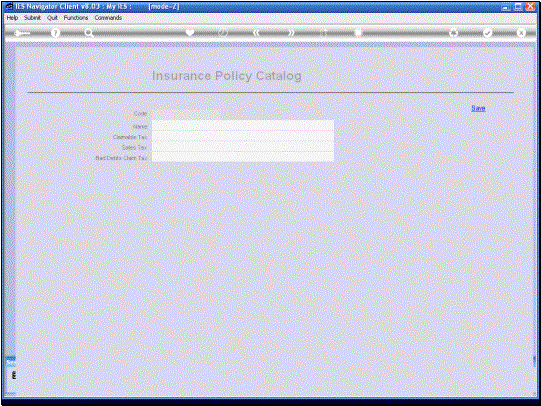
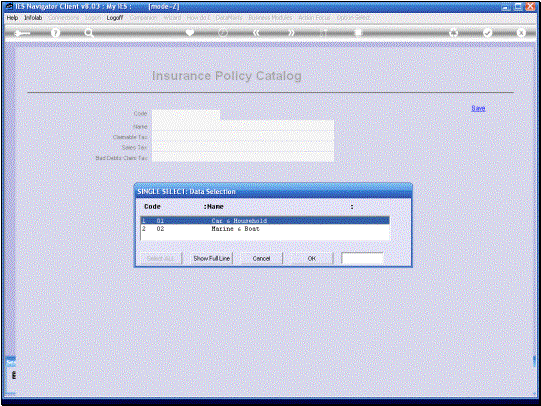
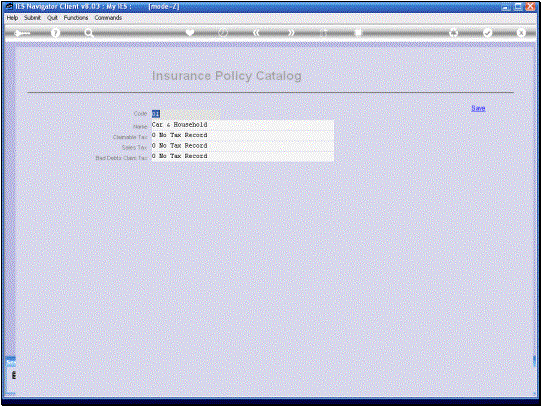
In this example we have
a Type for Car and Household Insurance and we have a No Tax indication for
claimable Tax, Sales Tax and Bad Debts Claim Tax. Now what does this mean?
These Tax Indicators
determine how the Policy is dealt with when the Premiums are charged to the
Customer. If we are required to
charge Collectable Tax (which is called VAT or GCT, and by various Other names in different
countries), then we are expected or obliged to collect such Taxes. Then we will not have
the Zero or NO Tax record indicator here. We will have the appropriate Tax
Type associated with each of these categories. But in this case, we can
safely say that in this setup we are NOT obliged to charge Tax on the Policy
Premiums. We will now look at
another example where we do have the Taxes specified. |
|
|
|
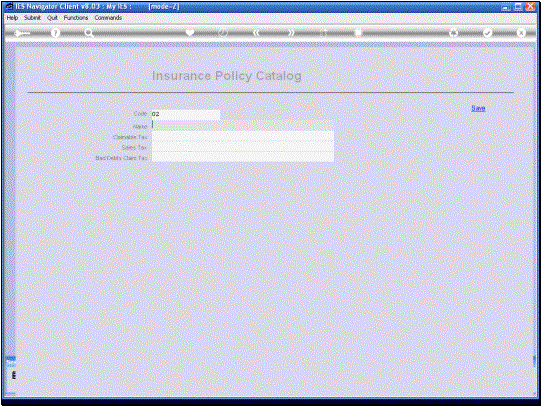
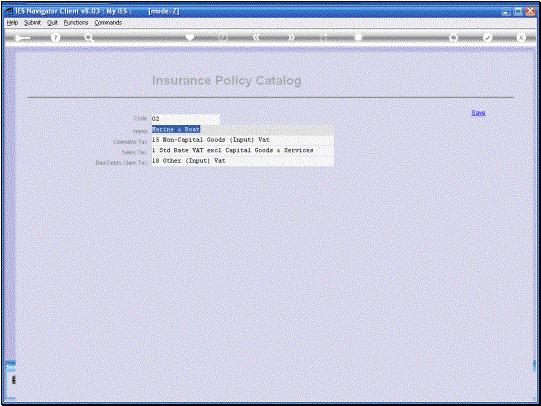
And in this example we
can see that we have a Tax Parameter specified for each category and what
this means is that in this setup, in this case we are looking at Tax examples
for South Africa. Of course these will be different in every country, but
there will be a Tax type for re-claimable Tax. In other words, that is
the input VAT in this case, that we can claim back from the Tax Receiver. The
Sales Tax indicator is the Tax type that is used to charge the Customer on
top of the Premium, whereas the Bad Debts Claim Tax indicator is the Tax type
the System will use for uncollected Premiums that are written off as Bad
Debts. |